We all have about 22,000 genes and sometimes we share enough genes with our family to be an almost identical copy of them. Although there may be 50 years between the 2 photos, their faces look the same thanks to the magic of these genes. There are some people who are carbon copies of their relatives, confirmed by their photos that simply blow us away.
Bright Side would like to share with you just how cool our genes can be with some exceptional photos we found.
1. “My mom and sister, both at age 6”
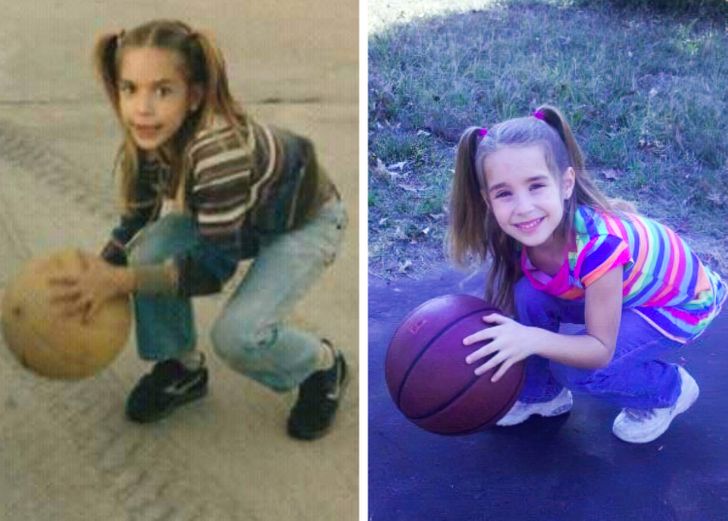
2. “My mom (left) age 4 in 1971. Me (right) age 4 in 2001. I see why people say we look alike.”
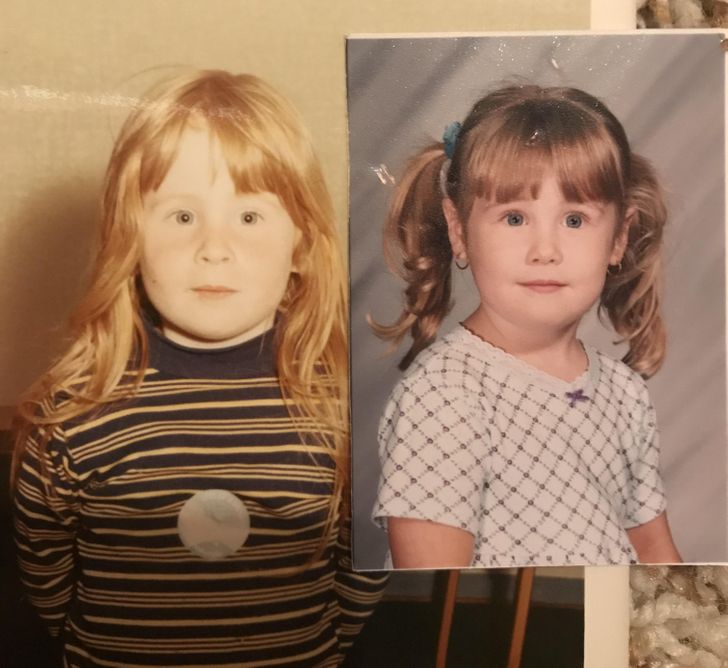
3. Grandmother 1941 and granddaughter 1999, same genes
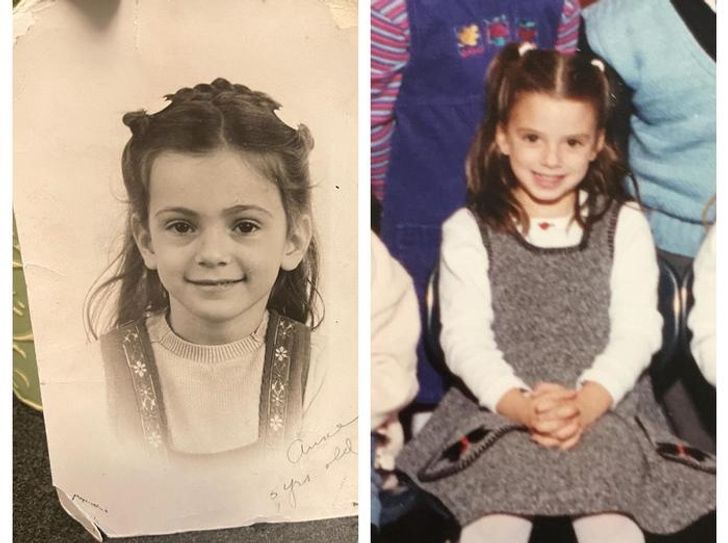
4. “Me, 1992. Mom, 1954.”
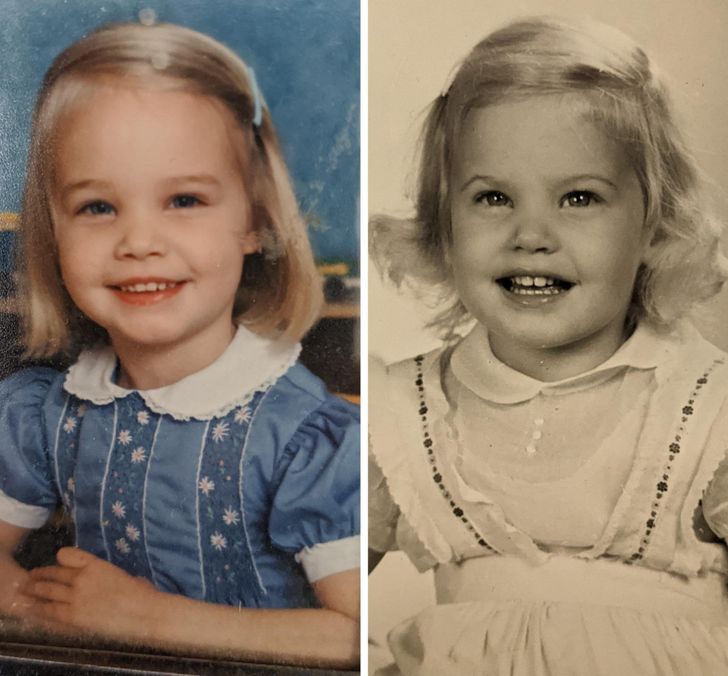
5. “Here’s me and my fraternal twin.”
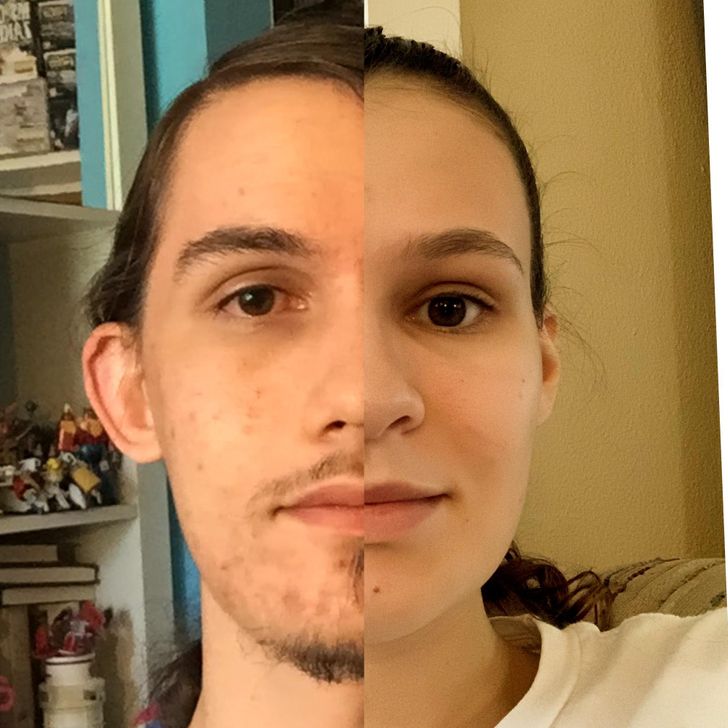

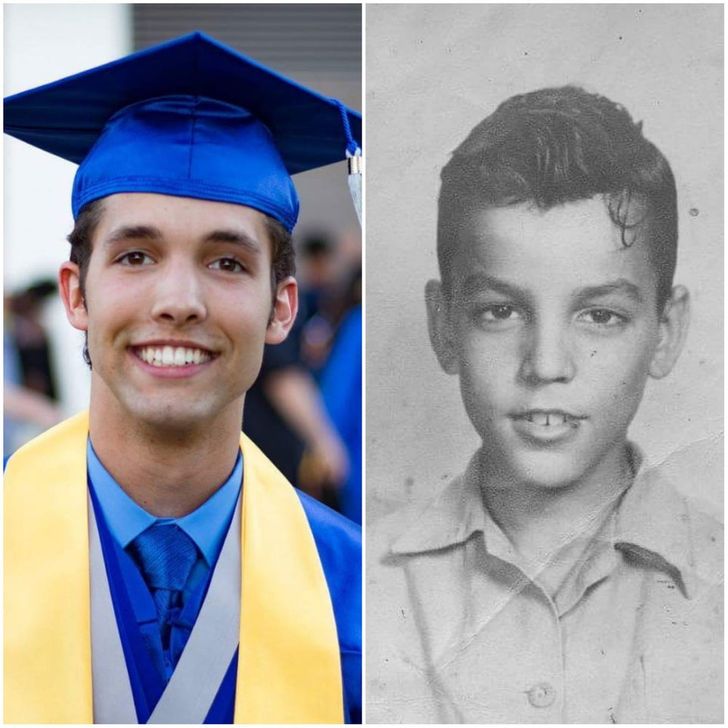
6. “Me on the left (circa ’90s, Canada) and my grand-dad (circa ’40s, Ireland).”
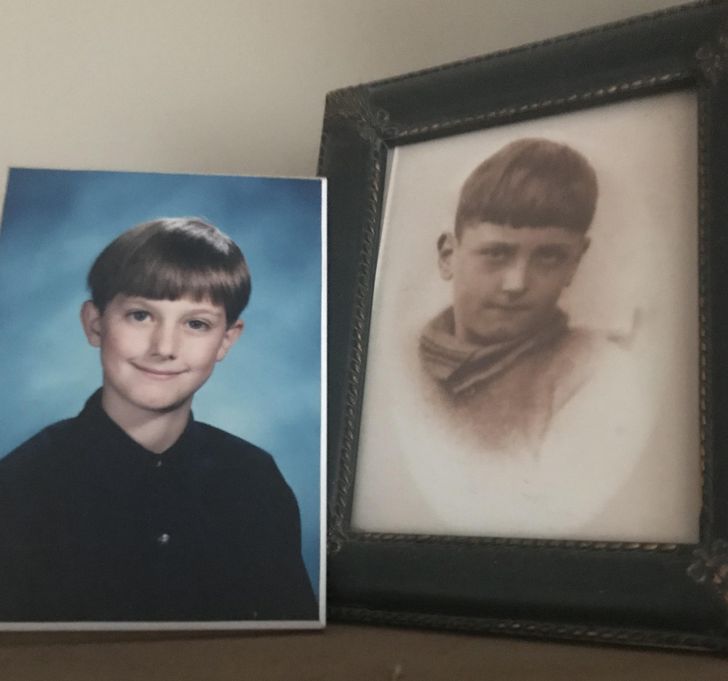

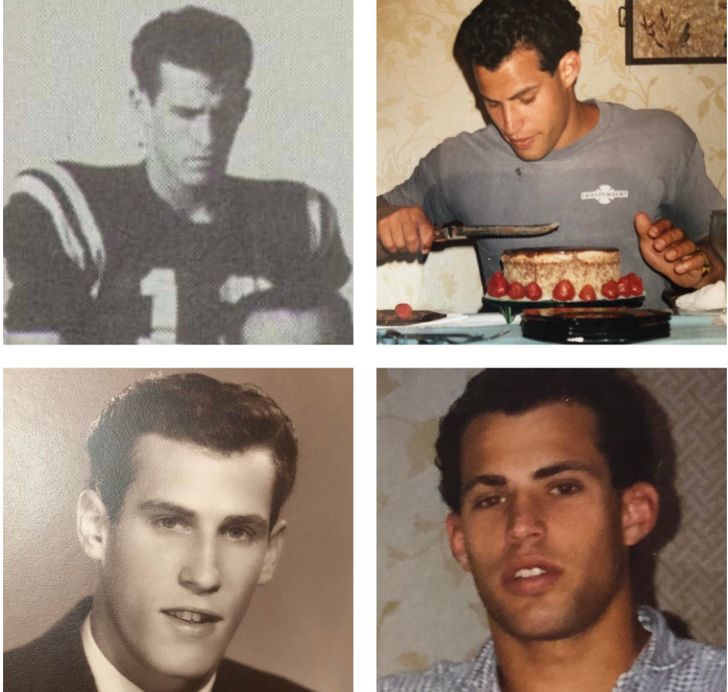
7. “My old man and me at the same age, 35 years apart.”
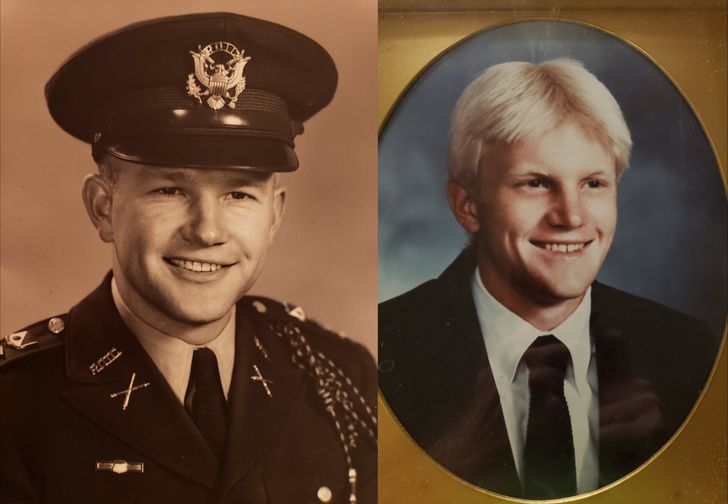

8. “Me in 1971 and my son in 1994”
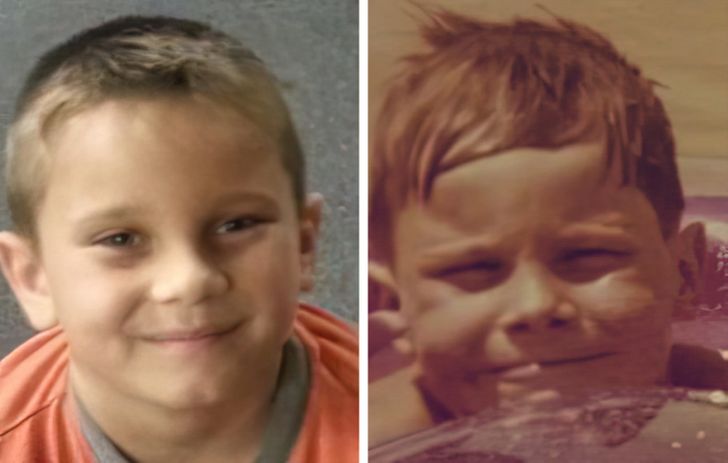

9. “My mother at age 21 (L) and me at age 27.”
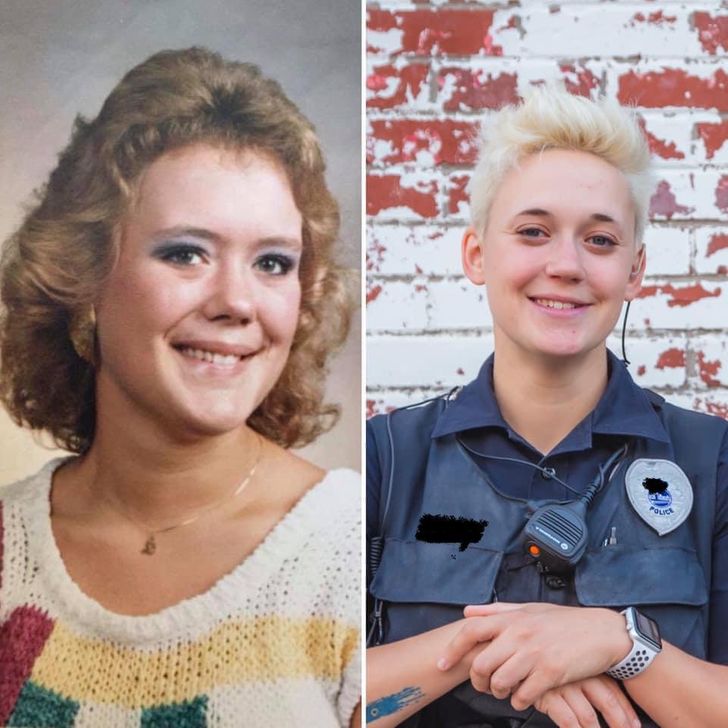

10. “My father, age 24 in 1951. And 24-year-old me.”
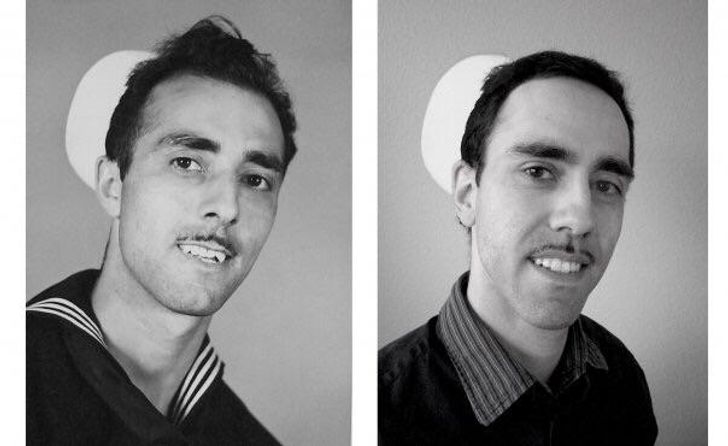

11. “I always knew that my mom and sister looked alike, but seeing them side by side is uncanny.”
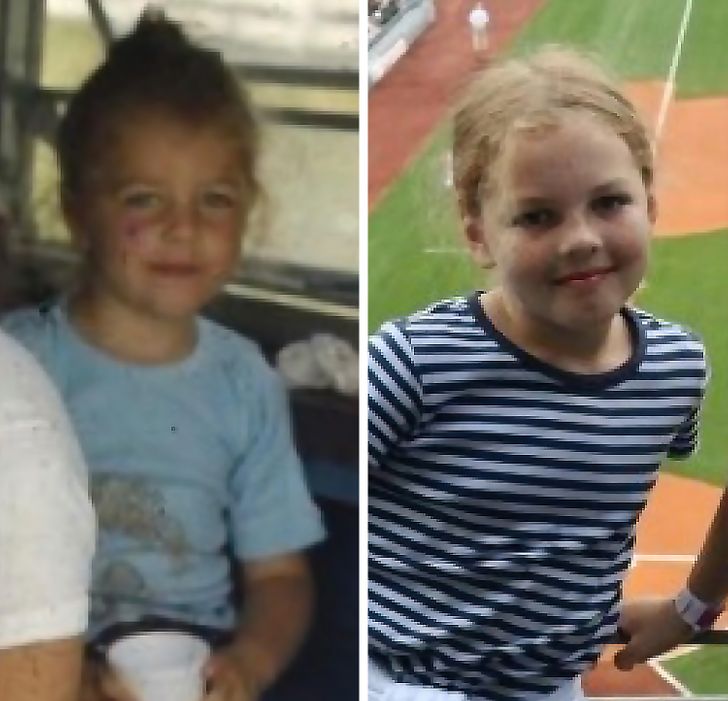

12. “My brother (2016) and my grandfather (1948)”
13. “I’ve been told a lot that I look like my Finnish grandma.”
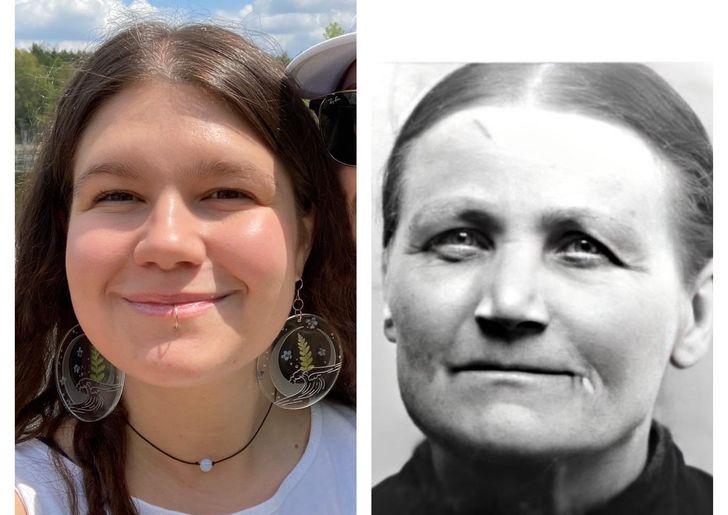

14. “My dad 1958… Me 1988.”

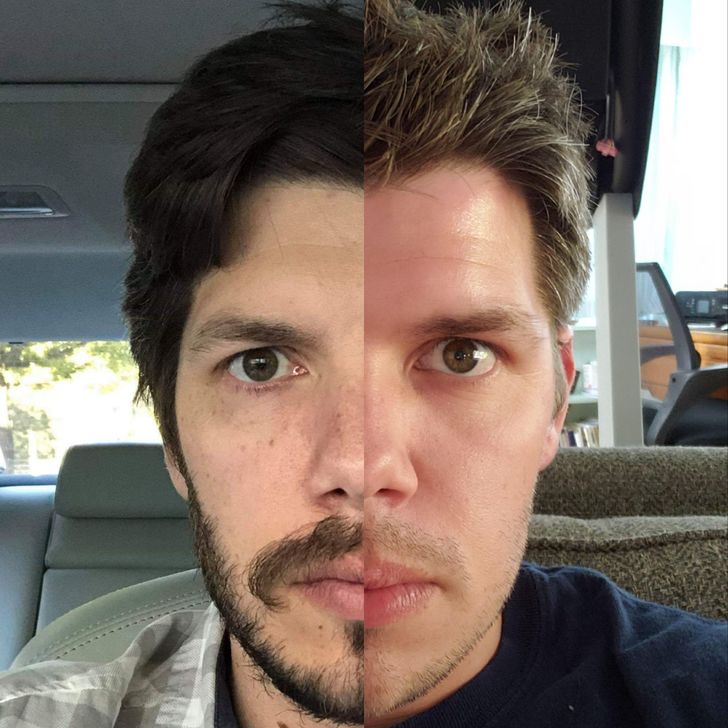
15. “Side-by-side comparison of my identical twin and me.”

Who do you look most like in your family? Share a photo of someone you look like so that we can compare!
Preview photo credit mrobry / Pikabu
Meg Foster was the movie star whose sky blue eyes drove people wild – sit down before seeing her today, 76
That we are all destined to grow old and grey is an immutable fact of life (for now, at least, who knows what the future holds with regards to technology and science).
It doesn’t matter how much money we have, how strictly we control our diet or exercise, how much sleep we get, or what we do for a living… sure, we might age differently, but in the end we’re all headed in the same direction. It’s basic biology, and not something we can do too much about.
Which is why it’s somewhat amusing that we can still be shocked when we see the hand of Father Time working its magic. Perhaps you haven’t seen someone for years, only to be taken back by how much they’ve aged? Or you spot an old movie star you remember from your childhood, only now their hair is white, their youthful exuberance gone.
It’s an interesting thing actually, the way celebrities age. Their appearances change as they get older – just as with any human being – only their path to old age is documented for the whole world to see. Be it from film to film, red carpet to red carpet, they leave a trail one can literally follow with their finger.
Now, time for today’s not-so-subtle segway: who remembers Meg Foster?
Of course you do! With her captivating, icy blue eyes, piercing gaze and raw beauty, how could you not? The American actress made her acting debut alongside Michael Douglas in Adam at 6am (1970), going on to star in numerous projects including The Six Million Dollar Man, Bonanza, The Twilight Zone and Murder, She Wrote.
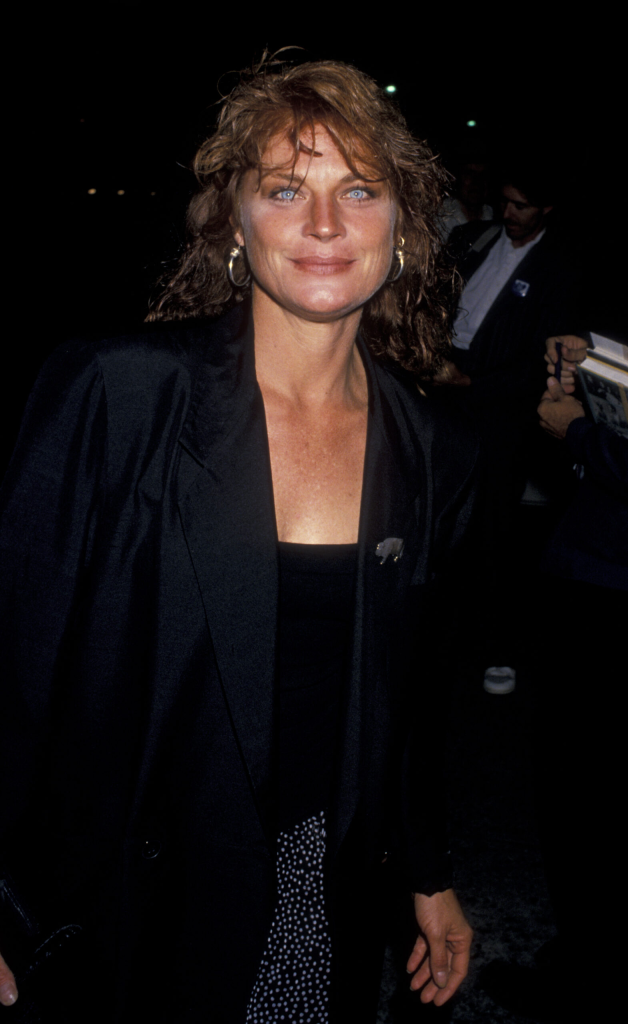

Once a burgeoning talent and in-demand actress, Foster’s star has steadily shrunk from the limelight in the last two decades. These days she looks virtually unrecognizable from the woman who Mademoiselle magazine said had “the eyes of 1979”.
I mean, that’s hardly a surprise given that she’s now 76 years old, but it appears that people on the internet simply can’t grasp just how much she’s changed. We’ll be honest, some of the comments to be found are borderline cruel, while others simply reinforce the idea that the actress looks nothing like she did.
That said, we think that her decision to age naturally – without resorting to the plastic surgery that has become so commonplace in the film and TV industry – should be commended, not lambasted.
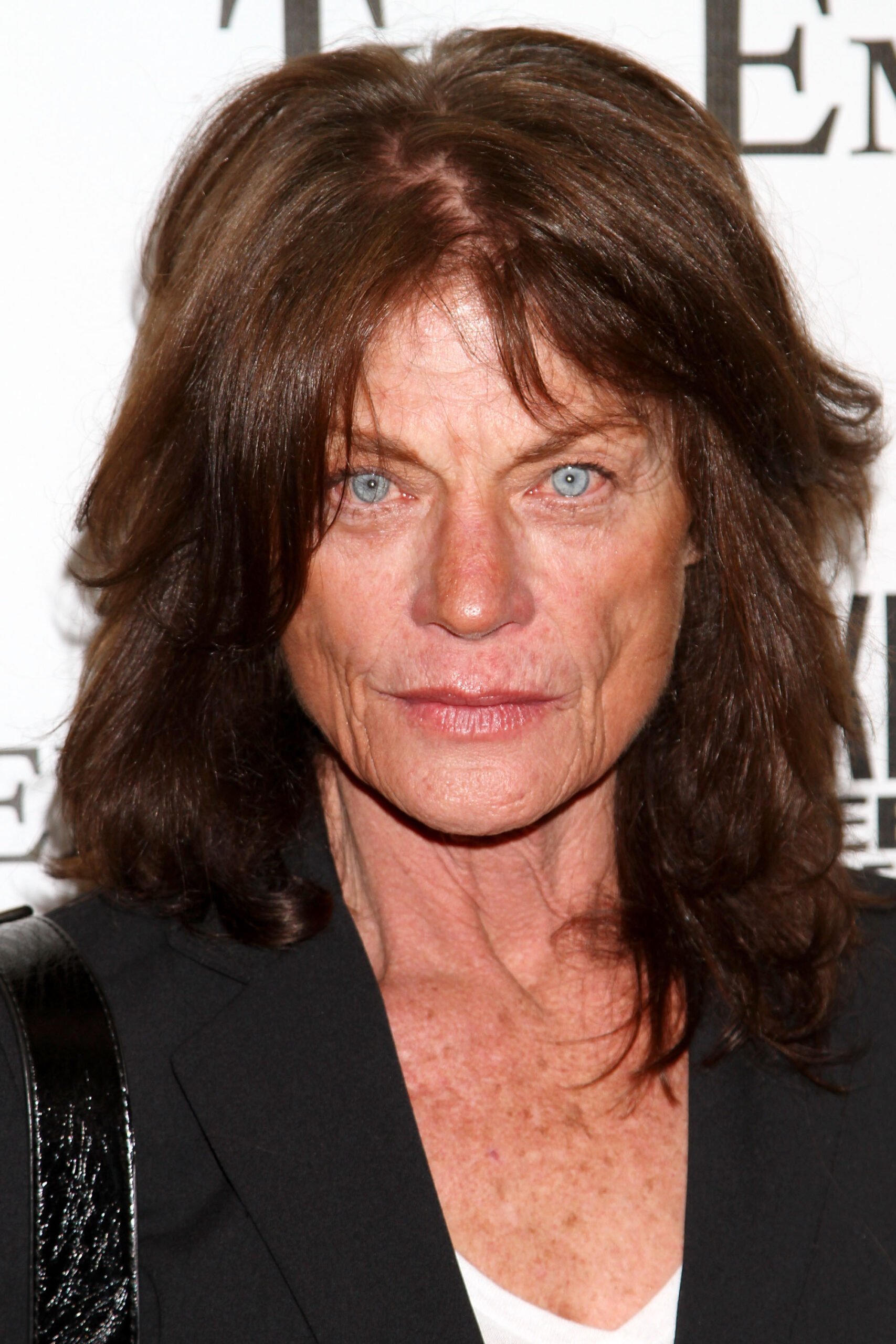

In any case, Foster continues to work within film and TV, as well as reportedly breeding horses from a large range which she owns by herself.
Do you remember Meg Foster? What do you think to how she looks now? Let us know in the comments.



Leave a Reply