Smartphones have become an inseparable part of modern life, revolutionizing communication, work, and entertainment. However, excessive smartphone use (ESU) has been linked to various negative consequences, including addiction-like behaviors, impaired mental health, and diminished attention spans. Recent studies suggest that smartphone-related cues can trigger neural responses similar to those seen in substance addiction, reinforcing compulsive usage patterns. Understanding the effects of smartphone restriction on cue-related neural activity can provide valuable insights into developing interventions for individuals struggling with ESU.
The Role of Cue Reactivity in Smartphone Use

Cue reactivity (CR) refers to the brain’s response to stimuli associated with a habitual or addictive behavior. In the case of smartphone use, cues may include notification sounds, phone screens lighting up, or simply seeing a smartphone in one’s environment. These cues can activate reward-related brain regions, reinforcing the compulsive urge to check the device.
Research has shown that individuals with excessive smartphone use exhibit heightened neural responses to smartphone-related cues, similar to those observed in substance addiction. This heightened sensitivity may contribute to difficulty in controlling smartphone usage, leading to a cycle of compulsive checking and craving.
Investigating Neural Activity Changes Through Smartphone Restriction
To better understand how short-term smartphone restriction influences brain activity, researchers conducted a study using functional MRI (fMRI) to measure changes in cue-related neural responses over 72 hours of smartphone abstinence. The study involved 25 young adults who were regular smartphone users.
Video : What Happens To Your Brain When You Mindlessly Scroll?
Study Design and Methods
- Participants were instructed to refrain from using their smartphones for 72 hours.
- A cue-reactivity task was designed, where participants were exposed to images of smartphones (both active and inactive) as well as neutral objects.
- Functional MRI scans were conducted before and after the restriction period to analyze changes in brain activity.
- Psychometric assessments were used to measure craving, self-control, and emotional responses associated with smartphone use.
Key Findings: How the Brain Adapts to Smartphone Restriction
1. Reduced Activation in the Reward System
One of the most striking findings was a significant reduction in activity in the nucleus accumbens and anterior cingulate cortex after 72 hours of smartphone restriction. These brain regions are heavily involved in reward processing and habit formation.
- The nucleus accumbens is associated with motivation and reinforcement learning. High activation in this area suggests strong craving and compulsive behavior.
- The anterior cingulate cortex plays a role in decision-making and impulse control. Reduced activity here indicates that participants may have experienced less compulsion to check their smartphones.
These findings suggest that even a short break from smartphone use can lead to neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to become less reactive to smartphone-related cues.
2. Alterations in Dopamine and Serotonin-Linked Activity
Further analysis using neurotransmitter probability maps revealed that activity changes in the reward system were closely linked to dopamine and serotonin receptor probabilities.
- Dopamine is a key neurotransmitter in reward-seeking behavior and addiction.
- Serotonin is involved in mood regulation and impulse control.
The findings suggest that smartphone restriction may influence neurochemical processes that drive compulsive behaviors. This could explain why some people feel withdrawal-like symptoms, including restlessness and anxiety, when they suddenly stop using their phones.

3. Increased Engagement of the Parietal Cortex
Another notable result was the increased activity in the parietal cortex, a region associated with attentional control and sensory processing.
- This suggests that participants became more aware of their environment and less preoccupied with smartphone-related distractions.
- Heightened parietal cortex activity was correlated with reduced craving scores, indicating improved cognitive control over impulsive smartphone use.
This supports the idea that limiting smartphone use can enhance focus and attentional regulation, reducing dependency on digital devices.
4. Reduced Compulsive Checking Behavior
Behavioral assessments showed that participants experienced a significant decrease in the urge to check their smartphones over time. This aligns with the observed neural changes in reward sensitivity and impulse control.
Participants also reported improvements in:
- Sleep quality: Reduced exposure to blue light and nighttime scrolling led to better sleep patterns.
- Social interactions: Without constant phone distractions, participants engaged more with people around them.
- Mental well-being: Several individuals noted feeling less anxious and more present in their daily activities.
Implications for Smartphone Addiction and Digital Detox Strategies

The findings of this study have significant implications for individuals struggling with excessive smartphone use. While a complete break from smartphones may not be feasible for everyone, implementing digital detox strategies can help manage usage and mitigate negative effects.
1. Scheduled Smartphone Breaks
- Taking regular breaks from smartphone use, even for a few hours a day, can help reset neural responses to digital cues.
- Setting specific times for checking messages rather than responding to every notification can reduce compulsive checking.
2. Mindful Technology Use
- Practicing conscious smartphone use by turning off unnecessary notifications and using grayscale mode can help decrease reliance on digital stimuli.
- Engaging in non-digital hobbies, such as reading, exercise, or meditation, can strengthen attention control and reduce smartphone dependency.
3. Sleep Hygiene and Nighttime Restrictions
- Avoiding smartphone use one hour before bed can improve sleep quality by preventing blue light exposure.
- Using do not disturb or airplane mode at night can minimize the temptation to check notifications.
4. Awareness Campaigns and Education
- Schools, workplaces, and mental health professionals can promote awareness of the impact of excessive smartphone use on brain function.
- Implementing digital wellness programs can encourage balanced technology use.
Video : Cell Phones Affect Brain Activity

Conclusion: How Smartphone Restriction Reshapes the Brain
The study provides compelling evidence that even a short period of smartphone restriction can lead to measurable changes in brain activity. The observed reductions in reward-related neural responses, coupled with increased attentional control, suggest that limiting smartphone use can promote cognitive flexibility, impulse control, and overall mental well-being.
As smartphone addiction continues to be a growing concern, understanding the neurological basis of cue-reactivity and digital dependency is crucial. These findings highlight the importance of incorporating healthy technology habits to ensure that smartphones remain tools for convenience rather than sources of compulsive behavior.
By making small adjustments in smartphone usage, individuals can foster better focus, improved mental clarity, and greater overall life satisfaction. So, why not start with a 72-hour break and see how your brain adapts?
Tragic Loss of Parents of Six During First Family Vacation

While on their first family vacation in Florida, six-time parents Brian Warter, 51, and Erica Wishart, 48, encountered an unbelievable tragedy.
On June 20, a tragic event happened when they were swimming off Hutchinson Island with two of their kids. Brian and Erica were left to the mercy of the strong ocean currents, even though the adolescents were able to rescue themselves.

Rescue efforts were started as soon as emergency personnel arrived. But despite everything they did, Brian and Erica were unfortunately declared dead at a local hospital, unable to be saved.
The water conditions were extremely dangerous on the day the couple perished. Red flags were flown along the beach, according to Cory Pippen of Martin County Fire Rescue, to warn swimmers of the hazardous riptide conditions. These flags are intended to alert beachgoers to possible aquatic dangers, like powerful rip currents.

After more than a year of dating, Brian and Erica got engaged. According to CBS 12 News, they intended to wed once their kids graduated from college. The family had been looking forward to this much-needed vacation for a long time. They took their kids along.
Brian’s father, Larry Warter, put their joy into words when he said, “They were so thrilled, they couldn’t see straight about going down.” It had never happened before. The experiment was this one. All six of their children were born together. It had taken them more than a month to plan.”
The overwhelming support that Brian’s family received from friends and relatives as well as the community left them in shock. Larry Warter conveyed his appreciation by saying, “Offers of assistance and other things have poured in.” We didn’t realize that we weren’t experiencing this alone.
A GoFundMe website was created in the couple’s memory, and Wayne Sallurday wrote a moving ode to Erica on it. He praised her as a remarkable individual, a devoted teacher, a caring mother, and someone who occasionally volunteered at her neighborhood church. He underlined that Erica was among the kindest people he had ever met.
Important information about rip currents is provided by the National Weather Service, which emphasizes that although they do not drag swimmers underwater, they can swiftly wear them out. In these kinds of situations, maintaining composure is essential.
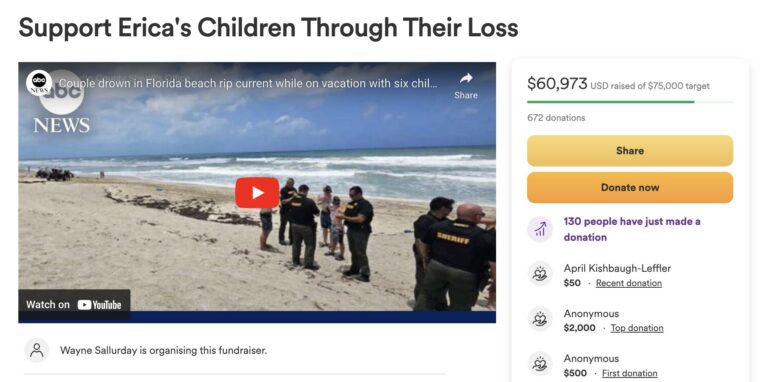
It is advised on the website that swimming against a rip current will simply sap your energy, which is necessary for survival and escape. Avoid attempting to swim straight up to the coast. Swim parallel to the coast until you are no longer pulled by the current. Swim at an angle away from the current and toward the shore once you are free of its pull. Additionally, the service exhorts swimmers to always swim in pairs and to follow the maxim “If in doubt, don’t go out!”
This terrible incident serves as a somber reminder of the risks presented by rip currents and the importance of listening to safety advisories when swimming. Peace be with Brian and Erica.
Please use Facebook to SHARE this post with your loved ones.



Leave a Reply