Have you ever visited a history museum or a battlefield with your school, when the teacher would give you a cannonball to hold and demonstrate how heavy it was, describing the sounds of battles and explosions in the open field? These experiences encouraged people to think, and provided a glimpse into our history and the physical reminders of conflicts that defined a country.
Cannonballs, the huge iron balls that used to roll out of the barrels of cannons, are typical relics of warfare of earlier centuries. Its basic yet effective structure was instrumental in battles from the medieval period up to the 19th century. Made from solid or hollow iron, these round shaped projectiles were used to knock down walls, disperse the enemies and to pierce through the sides of the enemy ships.
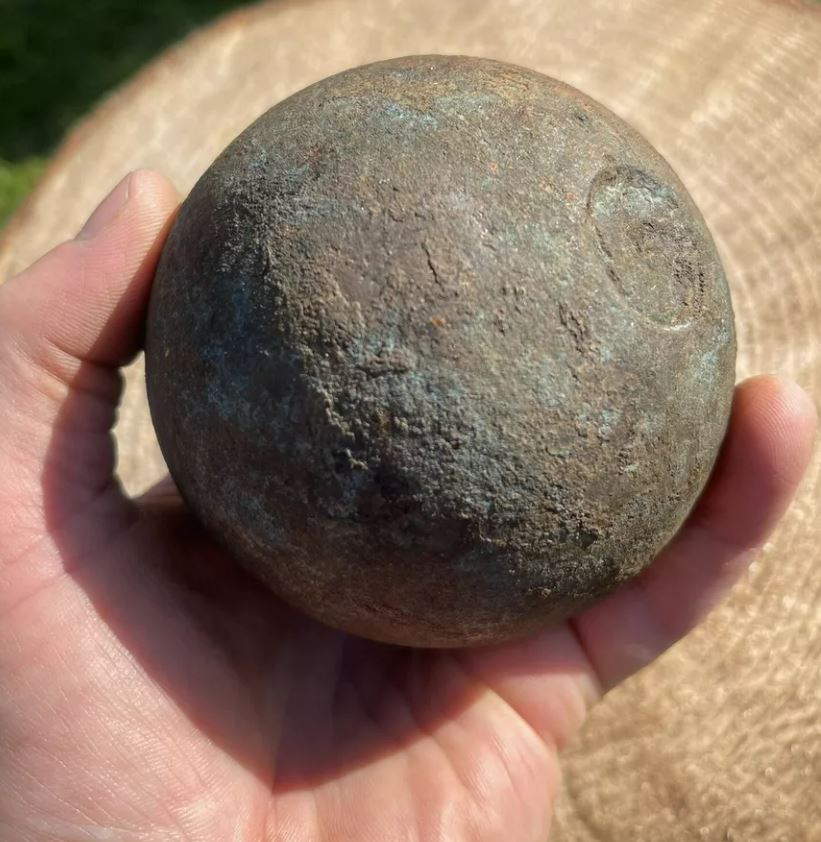

Cannonballs provide a rich understanding of how wars have been fought and the technologies used in the course of history. Every cannonball found or conserved today has a tale of ancient battles and the unrelenting search for military improvement. They were not just weapons of the warfare but also means that played a role in determining the fate of major battles and thus history. Their application and evolution offer an interesting insight into the creativity and adaptability of the military engineers of the past.
To those who collect antiques, an old cannonball is a precious find, a piece that tells a story of great history. People keep these artifacts as trophies for their historical value and the tales that are told by the rust marks on the items. But it is important that collectors do not mishandle these pieces as some of the older cannonballs may still contain unexploded explosives
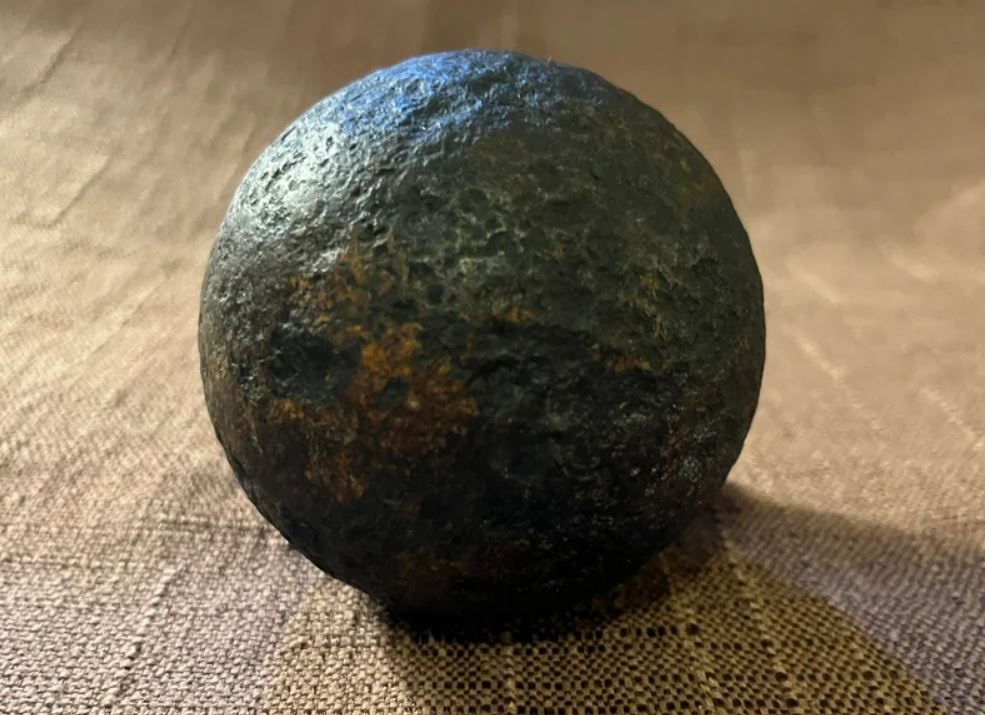

Thinking about the cannonball, we recall that people are capable of both dеstruсtiоn and innovation. Nowadays, as we showcase these relics in museums or preserve them as antiques, they become sources of information and topics for discussion that can pique the curiosity of people and make them more aware of history.
In conclusion, whether one considers cannonballs to be valuable collectibles or relics of the past, they remind us to look into the past to learn more about our forebears’ victories and tribulations. They urge people to protect and cherish the culture and history so that the coming generations may be able to understand and feel it as we do.
How should you react to survive when you suddenly fall into deep water without knowing how to swim?
Falling into deep water unexpectedly can be a terrifying experience, especially if you don’t know how to swim. Panic sets in, your instincts tell you to struggle, and before you know it, you’re exhausted and in real danger. However, survival in such a situation is entirely possible if you remain calm and follow a set of simple but life-saving steps.
According to Dr. Nash and his team of researchers, the key to survival is overcoming fear instincts and following five crucial steps. These steps are designed to help anyone—regardless of swimming ability—stay afloat, breathe, and increase their chances of rescue. Let’s dive into these life-saving techniques.
1. Stay Calm and Relax to Achieve Natural Buoyancy
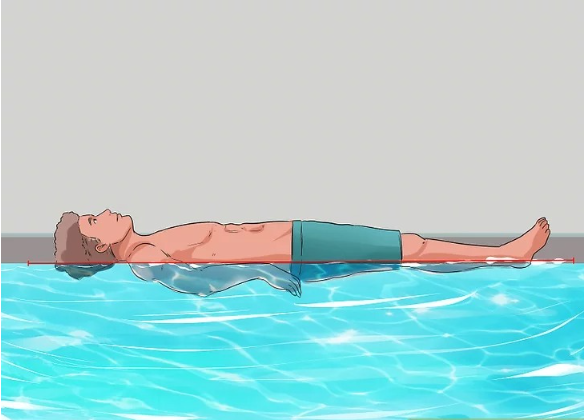
The first and most critical step is to fight the urge to struggle. Many people instinctively flail their arms and legs in a desperate attempt to stay above water. However, this only wastes energy and causes faster exhaustion.
Instead, take a deep breath and allow your body to relax. When you stop panicking, your body will naturally float closer to the water’s surface. The human body is slightly less dense than water, meaning that if you remain still, you can achieve buoyancy without much effort.
2. Tilt Your Head Back to Keep Your Airway Clear
Once you’ve calmed yourself and started floating, you need to ensure that you can breathe. The best way to do this is to tilt your head back, keeping your face above the water.
Try not to move too much, as sudden movements can make you sink slightly. If you feel yourself going under, resist the urge to panic—simply take a deep breath, relax your muscles, and allow yourself to rise again.
Video : How to Survive if You Fall in Water – Prevent Yourself From Drowning – Survival Techniques
3. Breathe Slowly and Avoid Inhaling Water
Now that your nose and mouth are above water, it’s time to focus on breathing. Many people instinctively gasp for air, but this can lead to choking if water splashes into your mouth. Instead, practice controlled breathing:
- Exhale slowly through your nose to clear any water that may have entered.
- Inhale through your mouth in a controlled manner.
- If a wave covers your face, hold your breath momentarily, then resume normal breathing.
Even experienced swimmers can struggle if they inhale water, so maintaining steady breathing is crucial for survival.
4. Move Your Arms and Legs Gently to Stay Afloat
At this point, you should be floating on the water’s surface and breathing steadily. The next step is to use gentle, controlled movements to maintain your position.
- Use slow arm movements: Move your arms in a sweeping motion, like you’re making small circles in the water. This will help you stay afloat without expending too much energy.
- Legs should remain still if you don’t know how to kick properly: If you’re unsure how to tread water, keeping your legs still is often better than kicking randomly. Let them sink slightly while focusing on keeping your upper body above water.
The key here is to avoid frantic movements—slow and deliberate strokes will keep you afloat much longer.
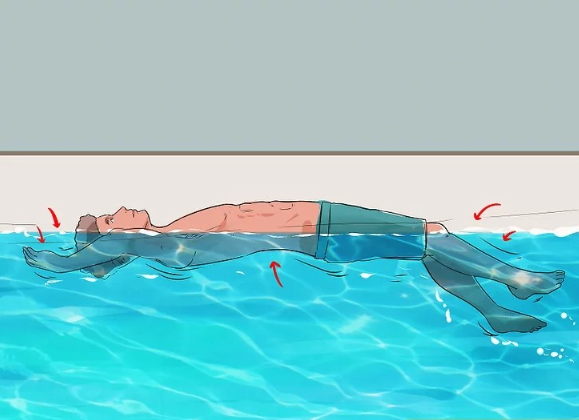
5. Look for Rescue Opportunities
Once you’ve gained control of your breathing and movements, your next priority is finding a way to safety.
- Scan your surroundings – Look for anything floating that you can grab onto, such as a buoy, a log, or even a piece of debris. Holding onto something will help you conserve energy.
- Check your distance from the shore – If you can see land, assess whether it’s possible to move toward it using slow, steady movements.
- Signal for help – If there are people nearby, shout for help. However, conserve energy by calling out only when necessary.
If you’re caught in a strong current, do not try to swim directly against it—this will only tire you out. Instead, swim diagonally at an angle to gradually move out of the current’s pull.
What to Do If You See Someone Drowning
If you witness someone struggling in deep water, it’s important to act quickly but safely. Jumping in to rescue them may seem like the right thing to do, but unless you’re a trained rescuer, it could put both of you at risk.
Instead, follow these steps:
- Shout instructions – Encourage the person to follow the survival steps above. Remind them to relax, tilt their head back, and float.
- Find a flotation device – If possible, throw a life jacket, a rope, or any floating object they can grab onto.
- Call emergency services – Immediately contact your local emergency number and provide details of the situation.
Video : How to get over fear of water – Feel safe on the deep end
Why Staying Calm is the Key to Survival
Many drowning incidents occur not because the victim physically sinks, but because they panic and exhaust themselves. Learning how to override panic instincts and follow a survival routine can mean the difference between life and death.
Dr. Nash explains:
“Whether you’re planning a vacation, taking a walk near a river, or going for a swim, knowing how to stay safe in water is crucial. These simple survival techniques can save your life or someone else’s.”
Final Thoughts
Surviving a fall into deep water without knowing how to swim is possible—but only if you remain calm and follow the right steps. By floating, maintaining steady breathing, and making slow movements, you can conserve energy and increase your chances of rescue.
Now that you know these survival strategies, share them with your friends and family. You never know when this knowledge might save a life!



Leave a Reply