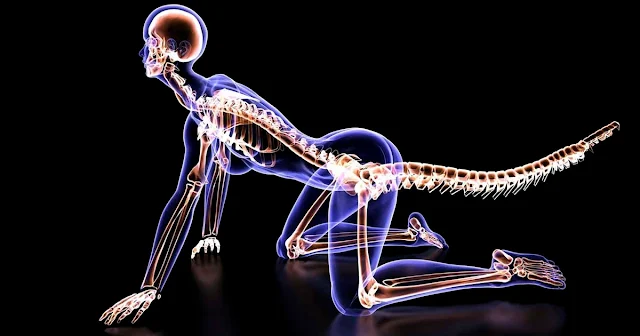
One of the most remarkable changes in human evolution is the loss of our tails, a transformation that occurred around 25 million years ago. This pivotal shift not only altered the trajectory of our species but also marked a significant moment in the evolutionary history of primates. While scientists have long speculated on why humans lost their tails, the genetic cause has remained elusive—until now. A recent study published in Nature has finally uncovered the genetic factors responsible for this evolutionary change.
The Quest to Understand Tail Loss
The journey to unravel the mystery of human tail loss began in an unexpected way. Bo Xia, a graduate student at New York University, was inspired to investigate the origins of the human tailbone after injuring his own coccyx. This personal curiosity led Xia and his team to embark on a groundbreaking scientific investigation.
Through careful research, the team focused on the TBXT gene, which plays a crucial role in regulating tail length in various species. Their research revealed a unique genetic mutation within this gene, providing a major breakthrough in understanding human evolution.
The Role of Jumping Genes
A key aspect of this discovery lies in the role of Alu elements, often called “jumping genes.” These genetic elements, specific to primates, can move within the genome and cause significant changes. The researchers found that Alu elements inserted themselves into the TBXT gene, triggering a chain reaction that led to the loss of our tails.
This insertion activated a process known as alternative splicing, where RNA molecules are cut and restructured, which ultimately led to the deletion of a crucial exon. This change altered the structure and function of the resulting protein, leading to the tail loss seen in humans.
Validation Through Mice Studies
To confirm their findings, the researchers engineered laboratory mice with the same genetic mutations found in humans and apes. These genetically altered mice lost their tails, providing compelling evidence that the identified mutation plays a crucial role in the absence of tails in humans and other primates.
However, the study also uncovered a downside to tail loss: an increased risk of neural tube defects, such as spina bifida. This finding highlights the complex balance between evolutionary benefits and potential genetic trade-offs.
The Broader Implications
This discovery has profound implications not just for understanding human evolution, but also for human anatomy and health. The loss of our tails was not a random event but a genetic adaptation with lasting consequences. It illustrates the complex relationship between genetic changes and the way they shape our physiology over time.
As we continue to study our evolutionary past, these findings remind us of the intricate process of natural selection and genetic innovation that has shaped humanity. This breakthrough also underscores the power of scientific inquiry in uncovering the mysteries of our origins, offering insight into the past that can help us understand our future.
The identification of the genetic reasons behind tail loss is a testament to the persistence of scientific exploration and the ongoing quest for knowledge about our evolutionary journey.
Minha cunhada exigiu que eu lhe desse meu bebê como presente de aniversário, mas ela recebeu exatamente o que merecia – História do dia

Minha cunhada sempre se sentiu no direito de ter o que quisesse, mas nada me preparou para sua demanda mais absurda até então — ela queria que eu tivesse um bebê só para que ela pudesse ficar com ele como um presente. Quando ela se recusou a aceitar um não como resposta, decidi lhe ensinar uma lição que ela nunca esqueceria.
Você acha que tem parentes loucos? Bem, deixe-me contar sobre os meus, e você pode mudar de ideia.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Harry e eu fomos casados por sete anos, juntos por quase quinze, e tivemos dois filhos maravilhosos, Maya e Luke.
Nossa pequena família era tudo para mim, mas quando se tratava da família extensa, as coisas não eram tão simples.
Percebi que havia algo errado com minha sogra, Charlotte, e minha cunhada, Candice, no primeiro dia em que as conheci.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Eu disse a mim mesmo que era só nervosismo, que eu estava pensando demais. Eu não tinha ideia de quantos problemas eles trariam para minha vida.
Antes do nosso casamento, Candice provou o quão egocêntrica ela era. Ela fez uma birra completa porque eu tive a audácia de escolher outra pessoa como minha dama de honra.
Pior ainda, ela disse que meu vestido era mais bonito que o dela. Como se meu casamento fosse girar em torno dela!

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Ela quase estragou o dia inteiro, mas felizmente Grace, a avó de Harry, interveio.
Grace era a única alma verdadeiramente gentil naquela família, além do meu marido. Infelizmente, ela morava longe demais para nos resgatar com frequência.
Mas pouco antes do trigésimo aniversário de Candice, algo aconteceu que me fez questionar a própria realidade.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Candice raramente nos visitava e, quando o fazia, mantinha distância das crianças, sempre reclamando que elas eram “muito barulhentas” ou “lhe davam dor de cabeça”.
Mas aquele dia foi diferente. Ela passou horas brincando com Maya, e algo sobre isso me deu um arrepio na espinha. No fim das contas, eu tinha todos os motivos para ficar preocupada.
Durante o jantar, Candice ficou olhando para mim e Harry. Eu sabia que ela queria atenção. Só não sabia o porquê.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Tenho um anúncio!” Sua voz ecoou pela sala de jantar. “Vou ser mãe!” ela deixou escapar.
Harry engasgou com a comida. Ele tossiu e pegou sua água. Eu congelei com meu garfo a meio caminho da boca.
“O quê?”, perguntei.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Harry limpou a boca. “Quem… é o pai?” Suas sobrancelhas franziram. “Você nem está namorando ninguém.”
Ele estava certo. O último namorado, ela fugiu depois que ela gritou com ele por não ter comprado uma bolsa cara para ela.
Candice acenou com a mão. “Na verdade, foi por isso que vim hoje.” Ela se endireitou na cadeira. “Os pais da minha filha serão vocês dois.”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Meu estômago se revirou. “O quê?!”
Ela suspirou como se eu fosse a louca. “Tenho quase trinta anos e não tenho marido.” Ela sorriu. “O presente de aniversário perfeito seria uma filha.”
Abri a boca, depois fechei. Meu cérebro lutou para processar suas palavras.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Harry esfregou as têmporas. “Você quer que Stephanie seja sua barriga de aluguel?”
Candice balançou a cabeça. “Não, eu quero que vocês dois tenham um bebê para mim.”
Coloquei minhas mãos na mesa. “Então, seria nosso filho, e você espera que a gente dê a você?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Não apenas dê—dê para mim de aniversário. Qual é o problema?” O tom dela era leve, casual, como se ela estivesse pedindo um suéter.
Olhei para ela. “Você realmente não vê problema algum?” Minha voz aumentou. “Harry e eu não vamos ter mais filhos. Não vou ter um bebê só para entregá-lo a você.”
Candice zombou. “Stephanie, você sempre foi tão egoísta.”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
A cadeira de Harry raspou no chão enquanto ele se sentava. “Não, Candice. Stephanie está certa. Não vamos fazer isso.”
“Mas por quê? Você já tem dois! Qual é o problema de ter mais um?” Sua voz atingiu um lamento agudo.
Cerrei os punhos. “Eu não sou uma incubadora! Uma criança não é um objeto! Uma criança é uma pessoa!”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Você simplesmente não quer que eu seja feliz! Você quer ser a única com filhos!” Candice gritou.
Harry bateu a mão na mesa. “Chega! Saia. Agora.”
O rosto de Candice ficou vermelho. Ela se levantou, tremendo de raiva. “Vou contar isso para a mamãe!” Ela foi até a porta, abriu-a e bateu-a atrás de si.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Eu exalei. “Como ela conseguiu inventar isso?”
Harry balançou a cabeça. “Ela perdeu completamente o controle.”
Candice ficou quieta por um tempo. Eu esperava que isso significasse que ela finalmente deixaria para lá. Eu deveria ter sabido melhor.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Uma tarde, Candice apareceu em nossa casa com Charlotte ao seu lado.
Os braços de Candice transbordavam com sacolas de compras de lojas de bebê. Meu primeiro pensamento foi que ela tinha decidido ser uma boa tia e trazer presentes para Maya e Luke. Mas o olhar presunçoso em seu rosto me disse o contrário.
Charlotte entrou sem esperar por um convite. Ela se sentou no sofá e gesticulou para que Harry e eu nos juntássemos a ela. Candice estava parada perto, sorrindo.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Candice me disse que você concordou em lhe dar um bebê”, disse Charlotte.
“O quê? Não, nós dissemos a ela que não faríamos isso”, eu disse.
“Por que não?” Charlotte perguntou.
“Porque é uma loucura”, respondeu Harry.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“É realmente tão difícil? Stephanie, como mulher, você deveria saber que quanto mais velha você fica, mais difícil é ter filhos. Candice já tem quase trinta anos”, argumentou Charlotte.
“Não vou entregar meu filho para sua filha, que não tem ideia do que significa ser mãe”, eu disse com firmeza.
“Isso não é verdade! Eu já comprei tudo!” Candice anunciou, tirando roupas de bebê e vestidos de suas bolsas.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Você percebe que um bebê não é uma boneca que você pode simplesmente vestir, certo? Bebês choram, gritam, cospem e fazem muitas coisas desagradáveis”, Harry apontou.
“Minha filha não será assim. Ela será como sua Maya — eu nunca vi Maya chorar”, Candice disse confiantemente.
“Isso é porque você nunca passou tempo suficiente com ela”, retruquei.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Então eu vou levar minha filha até você quando ela chorar”, disse Candice.
“Bebês choram dia e noite. Você está planejando trazê-la para mim toda vez?”, perguntei.
“Sim. Qual é o problema com isso?” Candice perguntou, genuinamente confusa.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Harry enterrou o rosto nas mãos. “Isso é impossível. Candice, você não está pronta para ser mãe. E pedir para alguém ter um filho para você é completamente insano”, ele disse.
“Mas você é meu irmão!” Candice gritou.
Enquanto eles discutiam, notei que Charlotte tinha desaparecido. Fui procurá-la e a encontrei em nosso quarto — furando nossas camisinhas.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“O que você está fazendo?!” eu gritei.
“Facilitando a vida de todos”, ela disse calmamente.
“Você perdeu a cabeça?!” eu gritei.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Escute, não seria difícil para você ter outro bebê, mas é difícil para Candice. Então eu decidi ajudar um pouco”, ela disse.
“Socorro?!” eu gritei. “Você está interferindo em nossas vidas pessoais !”
“Nem todo mundo tem a mesma sorte que você, tendo um marido como meu filho. Você deveria entender isso,” Charlotte respondeu.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Você está tratando a mim e ao seu filho como uma incubadora! Por que Candice não pode simplesmente ir a um doador de esperma?!” Eu gritei.
“Doadores são apenas pessoas aleatórias. Mas você e Harry já têm dois filhos saudáveis, então Candice saberia com certeza que seu bebê ficaria bem”, disse Charlotte.
“Esse seria nosso filho! Nosso! ” Eu gritei.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Mas você estaria fazendo isso por Candice, então seria filho dela “, argumentou Charlotte.
“Você realmente acha que eu daria meu filho para alguém que acredita que você pode escolher o sexo do bebê? Ou que bebês não choram?”, perguntei.
“Eu vou ajudá-la”, disse Charlotte.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Isso torna…” isso torna a situação ainda pior , eu queria dizer, mas me contive.
Uma ideia se formou na minha mente: uma maneira de ensinar uma lição para Candice e Charlotte e mostrar a todos o quão loucas elas eram.
“Sabe de uma coisa? Se você vai ajudar, então eu concordo,” eu disse.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Charlotte sorriu. “Finalmente! Por que você não disse isso antes?” ela disse, então foi contar a Candice as “boas notícias”.
Assim que eles saíram, Harry se virou para mim em choque. “Você realmente concordou com isso?”, ele perguntou.
“Eu tenho um plano”, eu disse.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Nos nove meses seguintes ao aniversário de Candice, desempenhei bem meu papel.
Sorri, toquei minha barriga com frequência e agi como a mulher grávida mais feliz.
Toda vez que Candice ligava, eu lhe assegurava que tudo estava indo bem. Eu até a deixava divagar sobre temas de berçário e nomes de bebês.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Foi exaustivo. Continuar a atuar me esgotou, mas eu tinha que ver isso até o fim.
Quando chegou a hora, anunciei que daria à luz em outra cidade. Candice fez beicinho, mas aceitou meu raciocínio — eu disse a ela que o “presente” tinha que permanecer como surpresa até seu aniversário. Afinal, era um presente, certo?
No grande dia, a família toda se reuniu para a revelação. Até Grace viajou para estar lá.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Pexels
Candice contou a todos sobre sua “grande surpresa”, criando momentos como se tivesse ganhado na loteria.
Harry e eu entramos quando todos estavam sentados. Eu segurava um canguru, enrolado com um laço gigante, embalando-o cuidadosamente. Candice arfou, suas mãos entrelaçadas na frente dela.
“Deixe-me vê-la!” ela gritou, tentando espiar lá dentro.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Ainda não”, eu disse. “Espere pelo grande momento.”
Finalmente, Candice se levantou, praticamente brilhando de excitação. “Tenho um anúncio muito especial!”, ela declarou. “Harry e Stephanie me deram o presente de aniversário mais incrível — um bebê!” Suspiros encheram a sala. Olhos fixos em nós.
Candice se virou, braços estendidos. “Okay, entregue-a agora!” Eu sorri e coloquei o carregador em suas mãos.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Candice arrancou o arco. Ela alcançou o interior do transportador com mãos trêmulas. Seus olhos brilharam de excitação. Então seu rosto se contorceu de horror.
“O QUE É ISSO?!” ela gritou, puxando uma boneca.
A sala ficou em silêncio. Todos os olhos estavam nela. Harry e eu caímos na gargalhada.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“O único bebê que você tem condições de cuidar”, eu disse, sorrindo.
O peito de Candice subia e descia rápido. Seus dedos cravaram nos membros de plástico da boneca. Ela olhou para mim com pura raiva.
“Mas você estava grávida!” ela gritou. “Eu vi sua barriga!”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Barrigas falsas”, eu disse, dando de ombros. “Eu saí da cidade para ‘dar à luz’ só para vender a ilusão.”
Candice soltou um soluço agudo. Charlotte engasgou e se levantou do assento.
“Sua bruxa sem coração!” Charlotte gritou.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“E quem exatamente é sem coração?” Eu rebati. “As pessoas que se recusaram a dar seus filhos? Ou aquelas que esperavam um bebê como se fosse um presente embrulhado?”
Candice apertou a boneca contra o peito. Lágrimas escorriam pelo seu rosto.
“Mas… mas eu já comprei tantos vestidos!” ela choramingou. “Quem eu vou vestir agora?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“A boneca funciona perfeitamente”, disse Harry, ainda rindo.
As mãos de Candice tremeram quando ela olhou para o brinquedo. Seu corpo inteiro tremeu.
Então notei Grace observando atentamente. Suas mãos enrugadas descansavam em seu colo. Seus olhos afiados iam de Candice a Charlotte.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Alguém pode me explicar o que está acontecendo aqui?” ela perguntou, com a voz firme.
Virei-me para ela. “Candice veio até nós há um ano exigindo que lhe déssemos um bebê de aniversário.”
O rosto de Grace se contorceu em confusão. “Você quer dizer… como uma barriga de aluguel? Ela tem problemas de saúde?”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Não,” Harry disse. “Nosso bebê.”
Grace franziu ainda mais a testa.
“Candice é perfeitamente saudável”, acrescentei. “Ela só não tem marido e achou que deveríamos dar a ela um filho.”

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
O rosto de Grace ficou vermelho de fúria. Ela se levantou do assento e apontou um dedo trêmulo para Candice e Charlotte.
“VOCÊS DOIS ESTÃO LOUCOS?!” ela rugiu.
Candice estremeceu. “O-o quê? O que há de errado com isso?” ela gaguejou.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Você é igualzinha à sua mãe, Candice! Eu avisei meu filho para não se casar com você, Charlotte, mas ele não ouviu! E esse é o resultado!” Grace cuspiu.
“Vovó, como você pôde dizer isso?!” Candice gritou.
“Estou dizendo a verdade!” Grace retrucou. Ela respirou fundo outra vez, então fixou os dois com um olhar de desgosto.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Estou tirando vocês dois do meu testamento.”
A sala ficou em silêncio. O patrimônio de Grace valia muito. Todos sabiam disso. Candice e Charlotte congelaram em choque.
“Você está falando sério?” Charlotte sussurrou, sua voz trêmula.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
“Absolutamente,” Grace disse friamente. “Eu não vou deixar pessoas insanas como você terem qualquer controle sobre minha riqueza.”
Um profundo e satisfeito senso de justiça me preencheu. Eu assisti enquanto a realização amanhecia neles.
“Mas—” Candice começou.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Grace levantou uma mão. “Chega. Estamos indo embora. Quero ver meus bisnetos — os verdadeiros.” Ela se virou para Harry e eu. “Vamos.”
Harry e eu não hesitamos. Nós nos levantamos e saímos, de mãos dadas. Atrás de nós, Candice soluçava histericamente.
Charlotte gritou de frustração. Mas não nos importamos. Eles tiveram exatamente o que mereciam.

Apenas para fins ilustrativos. | Fonte: Midjourney
Diga-nos o que você acha dessa história e compartilhe com seus amigos. Pode inspirá-los e alegrar o dia deles.
Se você gostou desta história, leia esta: Eu achava que minha sogra era simplesmente autoritária. Mas quando ela roubou os holofotes na nossa revelação de gênero, percebi que ela faria qualquer coisa para permanecer no centro de nossas vidas. Eu queria espaço. Ela se recusou a dar. Então descobri seu maior segredo — e o arrependimento a atingiu com mais força do que ela imaginava.



Leave a Reply